- Bioactive Compounds
- By Signaling Pathways
- PI3K/Akt/mTOR
- Epigenetics
- Methylation
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Protein Tyrosine Kinase
- Angiogenesis
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy
- ER stress & UPR
- JAK/STAT
- MAPK
- Cytoskeletal Signaling
- Cell Cycle
- TGF-beta/Smad
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair
- Compound Libraries
- Popular Compound Libraries
- Customize Library
- Clinical and FDA-approved Related
- Bioactive Compound Libraries
- Inhibitor Related
- Natural Product Related
- Metabolism Related
- Cell Death Related
- By Signaling Pathway
- By Disease
- Anti-infection and Antiviral Related
- Neuronal and Immunology Related
- Fragment and Covalent Related
- FDA-approved Drug Library
- FDA-approved & Passed Phase I Drug Library
- Preclinical/Clinical Compound Library
- Bioactive Compound Library-I
- Bioactive Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Express-Pick Library
- Natural Product Library
- Human Endogenous Metabolite Compound Library
- Alkaloid Compound LibraryNew
- Angiogenesis Related compound Library
- Anti-Aging Compound Library
- Anti-alzheimer Disease Compound Library
- Antibiotics compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library
- Anti-cancer Compound Library-Ⅱ
- Anti-cancer Metabolism Compound Library
- Anti-Cardiovascular Disease Compound Library
- Anti-diabetic Compound Library
- Anti-infection Compound Library
- Antioxidant Compound Library
- Anti-parasitic Compound Library
- Antiviral Compound Library
- Apoptosis Compound Library
- Autophagy Compound Library
- Calcium Channel Blocker LibraryNew
- Cambridge Cancer Compound Library
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Cell Cycle compound library
- CNS-Penetrant Compound Library
- Covalent Inhibitor Library
- Cytokine Inhibitor LibraryNew
- Cytoskeletal Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library
- Drug-like Compound Library
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library
- Epigenetics Compound Library
- Exosome Secretion Related Compound LibraryNew
- FDA-approved Anticancer Drug LibraryNew
- Ferroptosis Compound Library
- Flavonoid Compound Library
- Fragment Library
- Glutamine Metabolism Compound Library
- Glycolysis Compound Library
- GPCR Compound Library
- Gut Microbial Metabolite Library
- HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library
- Highly Selective Inhibitor Library
- Histone modification compound library
- HTS Library for Drug Discovery
- Human Hormone Related Compound LibraryNew
- Human Transcription Factor Compound LibraryNew
- Immunology/Inflammation Compound Library
- Inhibitor Library
- Ion Channel Ligand Library
- JAK/STAT compound library
- Lipid Metabolism Compound LibraryNew
- Macrocyclic Compound Library
- MAPK Inhibitor Library
- Medicine Food Homology Compound Library
- Metabolism Compound Library
- Methylation Compound Library
- Mouse Metabolite Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Organic Compound Library
- Neuronal Signaling Compound Library
- NF-κB Signaling Compound Library
- Nucleoside Analogue Library
- Obesity Compound Library
- Oxidative Stress Compound LibraryNew
- Plant Extract Library
- Phenotypic Screening Library
- PI3K/Akt Inhibitor Library
- Protease Inhibitor Library
- Protein-protein Interaction Inhibitor Library
- Pyroptosis Compound Library
- Small Molecule Immuno-Oncology Compound Library
- Mitochondria-Targeted Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Differentiation Compound LibraryNew
- Stem Cell Signaling Compound Library
- Natural Phenol Compound LibraryNew
- Natural Terpenoid Compound LibraryNew
- TGF-beta/Smad compound library
- Traditional Chinese Medicine Library
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Library
- Ubiquitination Compound Library
-
Cherry Picking
You can personalize your library with chemicals from within Selleck's inventory. Build the right library for your research endeavors by choosing from compounds in all of our available libraries.
Please contact us at [email protected] to customize your library.
You could select:
- Antibodies
- Bioreagents
- qPCR
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(Low ROX)
- 2x SYBR Green qPCR Master Mix(High ROX)
- Protein Assay
- Protein A/G Magnetic Beads for IP
- Anti-Flag magnetic beads
- Anti-Flag Affinity Gel
- Anti-Myc magnetic beads
- Anti-HA magnetic beads
- Magnetic Separator
- Poly DYKDDDDK Tag Peptide lyophilized powder
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (EDTA-Free, 100X in DMSO)
- Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (2 Tubes, 100X)
- Cell Biology
- Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
- Animal Experiment
- Mouse Direct PCR Kit (For Genotyping)
- New Products
- Contact Us
Clofarabine
Synonyms: Clolar
Clofarabine (Clolar) inhibits the enzymatic activities of ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) (IC50 = 65 nM) and DNA polymerase. Clofarabine induces autophagy and apoptosis.
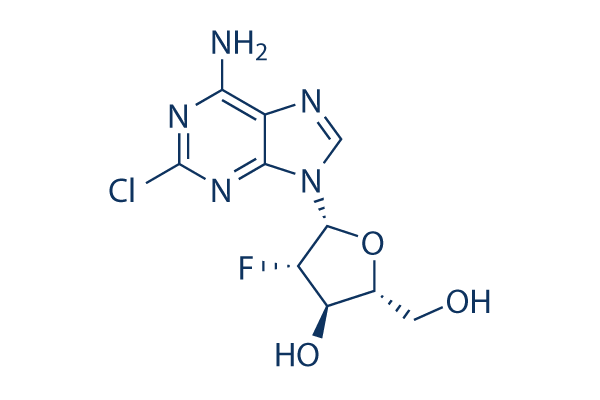
Clofarabine Chemical Structure
CAS No. 123318-82-1
Purity & Quality Control
Batch:
Purity:
99.90%
99.90
Clofarabine Related Products
| Related Targets | tRNA synthetase RdRp DNA synthesis helicase ribonucleotide reductase | Click to Expand |
|---|---|---|
| Related Products | Pidnarulex (CX-5461) SCR7 Favipiravir (T-705) RK-33 Carmofur Triapine (3-AP) B02 BMH-21 YK-4-279 Bergapten Tegafur (FT-207) Azaguanine-8 Halofuginone Adenine HCl Mizoribine Cyclocytidine HCl Thymidine APX-3330 Nedaplatin 6-Thio-dG Flupirtine maleate JH-RE-06 Pritelivir (BAY 57-1293) TK216 Amenamevir Madrasin Tubercidin BC-LI-0186 CRT0044876 PFM01 Adenine ML216 | Click to Expand |
| Related Compound Libraries | FDA-approved Drug Library Natural Product Library Apoptosis Compound Library DNA Damage/DNA Repair compound Library Cell Cycle compound library | Click to Expand |
Signaling Pathway
Cell Data
| Cell Lines | Assay Type | Concentration | Incubation Time | Formulation | Activity Description | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K562 cell | Cytotoxicity assay | Compound was tested for cytotoxicity against K562 cell lines, IC50=0.003 μM | 1732556 | |||
| HEp-2 cell | Cytotoxicity assay | Compound was tested for cytotoxicity against HEp-2 cell lines, IC50=0.012 μM | 1732556 | |||
| CCRF-CEM cell lines | Cytotoxicity assay | Compound was tested for cytotoxicity against CCRF-CEM cell lines, IC50=0.05 μM | 1732556 | |||
| L1210 cell | Cytotoxicity assay | Compound was tested for cytotoxicity against L1210 cell lines, IC50=2.3 μM | 1732556 | |||
| NCI-H23 | Cytotoxicity assay | 5 days | Cytotoxicity against human NCI-H23 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.04μM | 19929004 | ||
| PC3 | Cytotoxicity assay | 5 days | Cytotoxicity against human PC3 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.063μM | 19929004 | ||
| BT549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 5 days | Cytotoxicity against human BT549 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.065μM | 19929004 | ||
| HCT15 | Cytotoxicity assay | 5 days | Cytotoxicity against human HCT15 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.18μM | 19929004 | ||
| NCI-H23 | Cytostatic assay | 5 days | Cytostatic activity against human NCI-H23 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.04μM | 21711054 | ||
| MT4 | Cytostatic assay | 5 days | Cytostatic activity against human MT4 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.051μM | 21711054 | ||
| PC3 | Cytostatic assay | 5 days | Cytostatic activity against human PC3 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.063μM | 21711054 | ||
| BT549 | Cytostatic assay | 5 days | Cytostatic activity against human BT549 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.065μM | 21711054 | ||
| A549 | Cytostatic assay | 5 days | Cytostatic activity against human A549 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.086μM | 21711054 | ||
| HCT116 | Cytostatic assay | 5 days | Cytostatic activity against human HCT116 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.106μM | 21711054 | ||
| DU145 | Cytostatic assay | 5 days | Cytostatic activity against human DU145 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.125μM | 21711054 | ||
| HCT15 | Cytostatic assay | 5 days | Cytostatic activity against human HCT15 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=0.18μM | 21711054 | ||
| Hs578 | Cytostatic assay | 5 days | Cytostatic activity against human Hs578 cells after 5 days by SRB assay, GI50=1.241μM | 21711054 | ||
| HL60 | Cytostatic assay | 48 hrs | Cytostatic activity against human HL60 cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.1μM | 23820572 | ||
| A549 | Cytostatic assay | 48 hrs | Cytostatic activity against human A549 cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=8μM | 23820572 | ||
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 50 nM | 2 hrs | Potentiation of 5-Aza-C-induced antiviral activity against VSV-G pseudotyped HIV-1 NL4-3 infected in human U373-MAGI cells assessed as 5-Aza-C EC50 at 50 nM preincubated for 2 hrs followed by 5-Aza-C addition for 2 hrs and subsequent viral infection measu, EC50=30.4μM | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Antiviral assay | 50 nM | 4 hrs | Antiviral activity against VSV-G pseudotyped HIV-1 NL4-3 infected in human U373-MAGI cells assessed as reduction in viral infectivity at 50 nM incubated for 4 hrs prior to viral infection measured at 72 hrs post infection by flow cytometric analysis | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 200 nM | 6 hrs | Reduction in dGTP level in human U373-MAGI cells at 200 nM after 6 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 200 nM | 6 hrs | Reduction in dCTP level in human U373-MAGI cells at 200 nM after 6 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 200 nM | 6 hrs | Reduction in dATP level in human U373-MAGI cells at 200 nM after 6 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 50 nM | 2 hrs | Reduction in dCTP level in human U373-MAGI cells at 50 nM preincubated for 2 hrs followed by 5-aza-C addition measured after 4 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 200 nM | 2 hrs | Reduction in dCTP level in human U373-MAGI cells at 200 nM preincubated for 2 hrs followed by 5-aza-C addition measured after 4 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis relative to 5-aza-C | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 50 nM | 2 hrs | Increase in 5-aza-dCTP/dCTP ratio in human U373-MAGI cells at 50 nM preincubated for 2 hrs followed by 5-aza-dC addition measured after 4 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis relative to 5-aza-dC | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 200 nM | 2 hrs | Increase in 5-aza-dCTP/dCTP ratio in human U373-MAGI cells at 200 nM preincubated for 2 hrs followed by 5-aza-dC addition measured after 4 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis relative to 5-aza-dC | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 200 nM | 2 hrs | Reduction in dRGU-TP level in human U373-MAGI cells at 200 nM preincubated for 2 hrs followed by 5-aza-C addition measured after 4 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 200 nM | 2 hrs | Reduction in 5-aza-dCTP level in human U373-MAGI cells at 200 nM preincubated for 2 hrs followed by 5-aza-C addition measured after 4 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 200 nM | 2 hrs | Reduction in dCTP level in human U373-MAGI cells at 200 nM preincubated for 2 hrs followed by 5-aza-dC addition measured after 4 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis relative to 5-aza-dC | 27117260 | |
| U373-MAGI | Function assay | 50 nM | 2 hrs | Reduction in dCTP level in human U373-MAGI cells at 50 nM preincubated for 2 hrs followed by 5-aza-dC addition measured after 4 hrs by LC-MS/MS analysis relative to 5-aza-dC | 27117260 | |
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Granta | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human Granta cells assessed as decrease in cell viability after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.017μM | 30176535 | ||
| HL60 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HL60 cells assessed as decrease in cell viability after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.04μM | 30176535 | ||
| CCRF-CEM | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human CCRF-CEM cells assessed as decrease in cell viability after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.044μM | 30176535 | ||
| RL | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human RL cells assessed as decrease in cell viability after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.38μM | 30176535 | ||
| Click to View More Cell Line Experimental Data | ||||||
Biological Activity
| Description | Clofarabine (Clolar) inhibits the enzymatic activities of ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) (IC50 = 65 nM) and DNA polymerase. Clofarabine induces autophagy and apoptosis. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Targets |
|
| In vitro | ||||
| In vitro | Clofarabine is efficiently transported into cells via two facilitative or equilibrative nucleoside transporters, hENT1 and hENT2, and a concentrative nucleoside transporter, hCNT253. Clofarabine is phosphorylated in a stepwise manner by cytosolic kinases to the nucleotide analogues clofarabine 5′-mono-, di- and triphosphate following entry into cells, with Clofarabine triphosphate being the active form. Clofarabine 5′-mono-, di- and triphosphate are not substrates for nucleoside transporters and must be enzymatically converted by 5′-nucleotidase back to their dephosphorylated nucleoside form for transport out of the cell. Clofarabine triphosphate is a potent inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase (IC50 = 65 nM), presumably by binding to the allosteric site on the regulatory subunit. Clofarabine has also been shown to act directly on mitochondria by altering the transmembrane potential with release of cytochrome c, apoptotic-inducing factor (AIF), apoptosis protease-activating factor 1 (APAF1) and caspase 9 into the cytosol. Clofarabine demonstrates strong in vitro growth inhibition and cytotoxic activity (IC50 values = 0.028–0.29 μM) in a wide variety of leukaemia and solid tumour cell lines. Clofarabine has been shown to increase the activity of dCK in HL60 cells, and increases the formation of the mono-, di-, and triphosphates of ara-C in K562 cells36. [1] Clofarabine (10 μM) inhibits the repair initiated by 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide (4-HC), with inhibition peaking at the intracellular concentrations of 5 μM in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) lymphocytes. Clofarabine (10 μM) combined with 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide (4-HC) produces more than additive apoptotic cell death than the sum of each alone. [2] Clofarabine (1 μM) combined with ara-C (10 μM) results in a biochemical modulation of ara-CTP and synergistic cell kill in K562 cells. [3] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | ||
| In vivo | Clofarabine administered intraperitoneally has significant activity against a wide variety of human tumour xenografts implanted subcutaneously in athymic nude or severe combined immune deficiency mice. [1] | |
|---|---|---|
| NCT Number | Recruitment | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05917405 | Recruiting | Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Remission |
Nantes University Hospital |
September 14 2023 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03609814 | Completed | Hematologic Malignancies|Nonmalignant Diseases|Immunodeficiencies|Hemoglobinopathies|Genetic Inborn Errors of Metabolism|Fanconi''s Anemia|Thalassemia|Sickle Cell Disease |
University of California San Francisco |
January 26 2016 | -- |
Chemical Information & Solubility
| Molecular Weight | 303.68 | Formula | C10H11ClFN5O3 |
| CAS No. | 123318-82-1 | SDF | Download Clofarabine SDF |
| Smiles | C1=NC2=C(N=C(N=C2N1C3C(C(C(O3)CO)O)F)Cl)N | ||
| Storage (From the date of receipt) | |||
|
In vitro |
DMSO : 60 mg/mL ( (197.57 mM) Moisture-absorbing DMSO reduces solubility. Please use fresh DMSO.) Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molecular Weight Calculator |
|
In vivo Add solvents to the product individually and in order. |
In vivo Formulation Calculator |
||||
Preparing Stock Solutions
Molarity Calculator
In vivo Formulation Calculator (Clear solution)
Step 1: Enter information below (Recommended: An additional animal making an allowance for loss during the experiment)
mg/kg
g
μL
Step 2: Enter the in vivo formulation (This is only the calculator, not formulation. Please contact us first if there is no in vivo formulation at the solubility Section.)
% DMSO
%
% Tween 80
% ddH2O
%DMSO
%
Calculation results:
Working concentration: mg/ml;
Method for preparing DMSO master liquid: mg drug pre-dissolved in μL DMSO ( Master liquid concentration mg/mL, Please contact us first if the concentration exceeds the DMSO solubility of the batch of drug. )
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next addμL PEG300, mix and clarify, next addμL Tween 80, mix and clarify, next add μL ddH2O, mix and clarify.
Method for preparing in vivo formulation: Take μL DMSO master liquid, next add μL Corn oil, mix and clarify.
Note: 1. Please make sure the liquid is clear before adding the next solvent.
2. Be sure to add the solvent(s) in order. You must ensure that the solution obtained, in the previous addition, is a clear solution before proceeding to add the next solvent. Physical methods such
as vortex, ultrasound or hot water bath can be used to aid dissolving.
Tech Support
Answers to questions you may have can be found in the inhibitor handling instructions. Topics include how to prepare stock solutions, how to store inhibitors, and issues that need special attention for cell-based assays and animal experiments.
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
If you have any other enquiries, please leave a message.
* Indicates a Required Field
Tags: buy Clofarabine | Clofarabine supplier | purchase Clofarabine | Clofarabine cost | Clofarabine manufacturer | order Clofarabine | Clofarabine distributor